Across all sectors, automation technology is boosting the efficiency and accuracy of business processes. From virtual assistance to KPI planning, automation is now embedded into everyday practice.
Two types of automation that get a lot of attention are Intelligent Automation (also known as Intelligent Process Automation) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Each can lower operational costs and boost customer satisfaction – results we’re all looking to achieve. And even though these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are in fact quite different.
Let’s look at what defines these technologies, how they can be used and the pros and cons of each.
Intelligent Process Automation vs RPA: What You Need to Know
What is RPA?
Simply put, RPA is rules-based software programming that automates repetitive, mundane business tasks and processes. The types of actions that don’t require intelligence, analysis or special skills are ideally suited to RPA workflows.

For example, RPA can:
- Perform virtual assistant functions.
- Collect and transfer data among multiple spreadsheets or files.
- Tabulate results.
- Process invoices.
- Manage payroll.
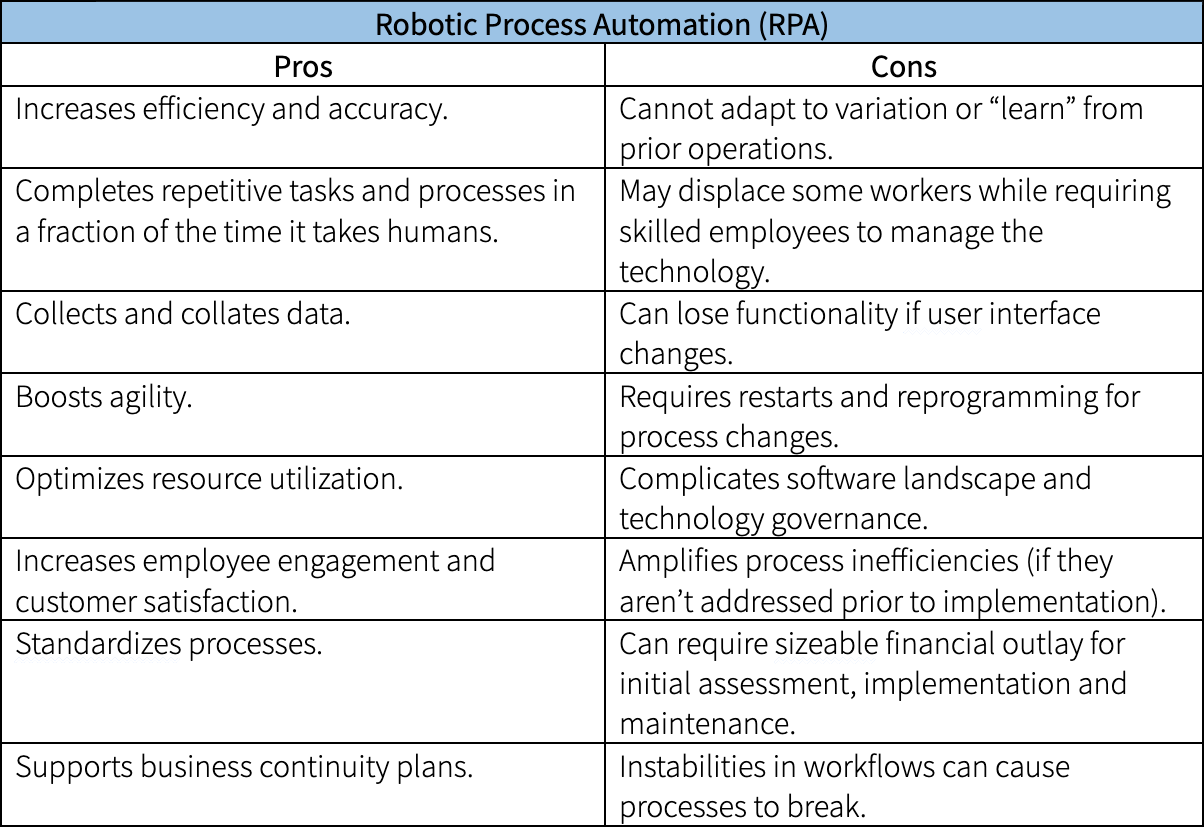
Pros and Cons of RPA
RPA can improve speed and accuracy for many tedious business processes by using bots. However, it cannot easily handle variation. Here’s an overview of what RPA does best and some of its limitations:
What is Intelligent Automation?
While RPA increases the efficiency and accuracy of well-defined business processes, they’re no longer enough to keep a modern organization running smoothly and efficiently.
Intelligent Automation is the next evolution of RPA – the “brain” to RPA’s “brawn.” Adding Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Business Process Management (BPM) and other technologies to build on the functions of RPA, Intelligent Automation can learn, reason and make decisions.

While Intelligent Automation maintains the speed and precision of RPA, its holistic approach – involving a mix of rule-based automation and AI’s analytical and predictive capabilities – can manage complex business processes. Intelligent Automation can respond to change, variety and circumstances that fall outside the boundaries of its scripts.
In addition, Intelligent Automation can analyze and interpret data to identify patterns, draw conclusions and make predictions. And significantly, it improves itself over time, driving better business outcomes and allowing human staff to work more creatively on new products and services.
Intelligent Automation can:
- Process unstructured data.
- Automate tasks that require judgment.
- Detect and adapt to change.
- Facilitate resource and KPI planning.
- Manage exceptions and make internal course adjustments.
Of course, just like with any technology, there are benefits and drawbacks to Intelligent Automation:
Conclusion
Although they are closely related, RPA and Intelligent Automation can serve different purposes within your organization. It’s not a case of Intelligent Automation vs Robotic Process Automation – adopting one does not mean you have to get rid of the other. In fact, RPA functions form part of the fabric of Intelligent Automation.
Intelligent Automation provides a holistic vehicle for digital transformation across your entire business. It helps improve customer experience, reduce operational costs, simplify governance and increase staff productivity.
The best approach to adopting and integrating process automation solutions is to craft a long-term strategy that maximizes the benefits of both RPA and Intelligent Automation based on a careful assessment of your company’s needs.
About Sutherland Robility
Kickstart your RPA journey today. Sutherland Robility supercharges your workflows and maximizes business outcomes with the same low-code design framework as traditional RPA software – at a fraction of the licensing cost.
Robility’s high-density design allows multiple bots to operate on a single virtual machine. Through high-efficiency digitization and data structuring features, it offers a simple system that doesn’t need new skill sets. Manage complex processes, large volumes of information and unrelated IT systems with minimal manual intervention.
Get in touch to find out more.



